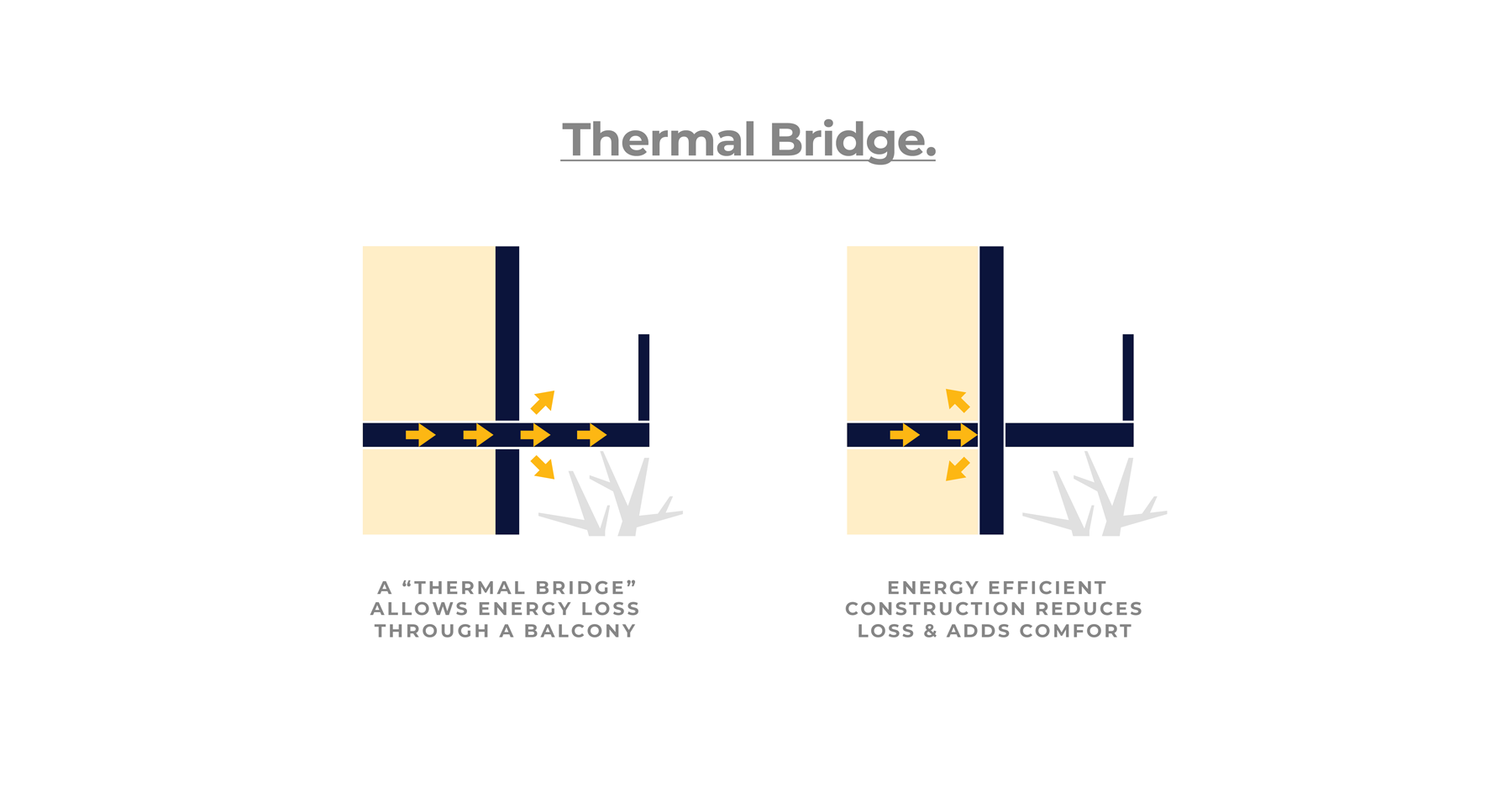
WHY DOES THERMAL BRIDGING MATTER?
In many older homes, numerous small gaps exist, allowing unconditioned air to seep in while conditioned air escapes. This undesirable airflow not only wastes energy but also diminishes the efficiency of heating and cooling systems, potentially leading to moisture issues and allowing dust, pollen, and other pollutants to infiltrate the home.
While thermal bridging can occur in various areas such as floors, balconies, and windowsills, it is most apparent in exterior walls. In many homes, insulation is typically placed between studs in the wall. However, the studs themselves can act as bridges for energy transfer between the indoors and outdoors. To address this issue, walls can be constructed with continuous insulation layers, increased spacing between studs, and intentional connections between materials.
The most sustainable home designs aim to eliminate thermal bridging entirely. This is achieved through meticulous carpentry and product installation by contractors, ensuring that no pathways for heat transfer exist through the building envelope.
HOW MUCH DOES IT COSTS?
Eliminating thermal bridging presents fewer challenges in new home construction than in renovation projects. While there are some additional costs involved in creating a continuous insulation layer and collaborating with highly skilled builders, the overall impact on building costs is minimal.
Nevertheless, since thermal bridging significantly contributes to energy loss, a home free from thermal bridging stands to benefit from reduced utility bills. This leads to a favorable return on the initial investment over time.
